Introduction to WANs
These are the major characteristics of WANs:
•They connect devices that are separated by wide geographical areas.
•They use the services of carriers such as the Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs), Sprint, MCI, VPM Internet Services, Inc., and Altantes.net.
•They use serial connections of various types to access bandwidth over large geographic areas.
WAN technology/terminology
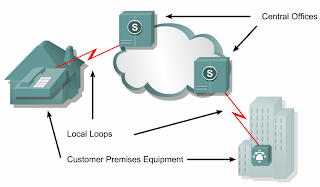
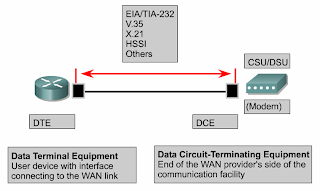
•Devices on the subscriber premises are called customer premises equipment (CPE).
•The subscriber owns the CPE or leases the CPE from the service provider.
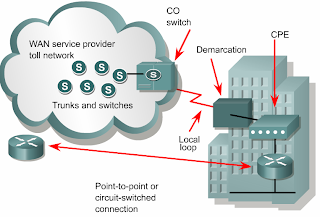
•A copper or fiber cable connects the CPE to the service provider’s nearest exchange or central office (CO).
•This cabling is often called the local loop, or "last-mile".
•A dialed call is connected locally to other local loops, or non-locally through a trunk to a primary center.
•It then goes to a sectional center and on to a regional or international carrier center as the call travels to its destination.
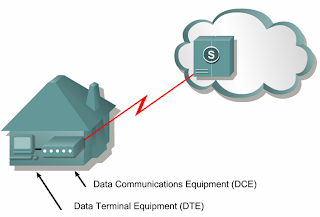
•Devices that put data on the local loop are called data circuit-terminating equipment, or data communications equipment (DCE).
•The customer devices that pass the data to the DCE are called data terminal equipment (DTE).
•The DCE primarily provides an interface for the DTE into the communication link on the WAN cloud.
WAN technology/terminology
•A dialed call is connected locally to other local loops, or non-locally through a trunk to a primary center.
•It then goes to a sectional center and on to a regional or international carrier center as the call travels to its destination.
•The DTE/DCE interface uses various physical layer protocols, such as High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI) and V.35.
•These protocols establish the codes and electrical parameters the devices use to communicate with each other.
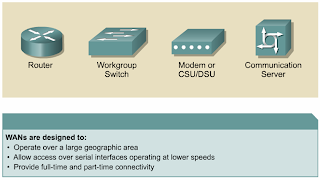
WAN Devices
•Routers offer many services, including internetworking and WAN interface ports.
•Switches in the WAN provide connectivity for voice, data, and video communication.
•Modems include interface voice-grade services, channel service units/digital service units (CSU/DSUs) that interface T1/E1 services, and Terminal Adapters/Network Termination 1 (TA/NT1s) that interface Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) services.
•Communication servers concentrate dial-in and dial-out user communication.
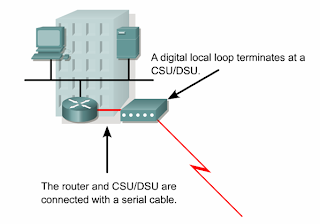
External CSU/DSU
•The CSU/DSU may also be built into the interface card in the router.
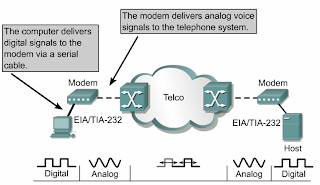
Modems
•Modems transmit data over voice-grade telephone lines by modulating and demodulating the signal.
•The digital signals are superimposed on an analog voice signal that is modulated for transmission.
•The modulated signal can be heard as a series of whistles by turning on the internal modem speaker.
•At the receiving end the analog signals are returned to their digital form, or demodulated.
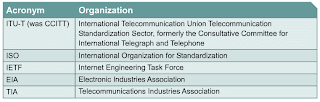
WAN Standards Organizations
•WAN standards typically describe both physical layer delivery methods and data link layer requirements, including physical addressing, flow control, and encapsulation.
•WAN standards are defined and managed by a number of recognized authorities.




No comments:
Post a Comment